Hydrophobic binary mixtures containing amphotericin B as lipophilic solutions for the treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis
- TR Number: 1054
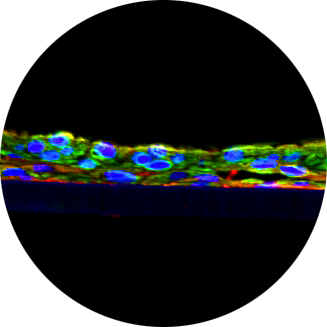
Cutaneous leishmaniasis, caused by Leishmania parasites, requires treatments with fewer side effects than those currently available. The development of a topical solution based on amphotericin B (AmB) was pursued. The considerable interest in deep eutectic solvents (DESs) and their remarkable advantages inspired the search for a suitable hydrophobic excipient. Various mixtures based on commonly used hydrogen bond donors (HBDs) and acceptors (HBAs) for DES preparations were explored. Initial physical and in-vitro screenings showed the potential of quaternary phosphonium salt-based mixtures. Through thermal analysis, it was determined that most of these mixtures did not exhibit eutectic behavior. X-ray scattering studies revealed a sponge-like nanoscale structure. The most promising formulation, based on a combination of trihexyl(tetradecyl)phosphonium chloride and 1-oleoyl-rac-glycerol, showed no deleterious effects through histological evaluation. AmB was fully solubilized at concentrations between 0.5 and 0.8 mg⋅mL-1, depending on the formulation. The monomeric state of AmB was observed by circular dichroism. In-vitro irritation tests demonstrated acceptable viability for AmBbased formulations up to 0.5 mg⋅mL-1. Additionally, an ex-vivo penetration study on pig ear skin revealed no transcutaneous passage, confirming AmB retention in healthy, unaffected skin.