Get the latest
Get MatTek offers and updates delivered to your inbox.
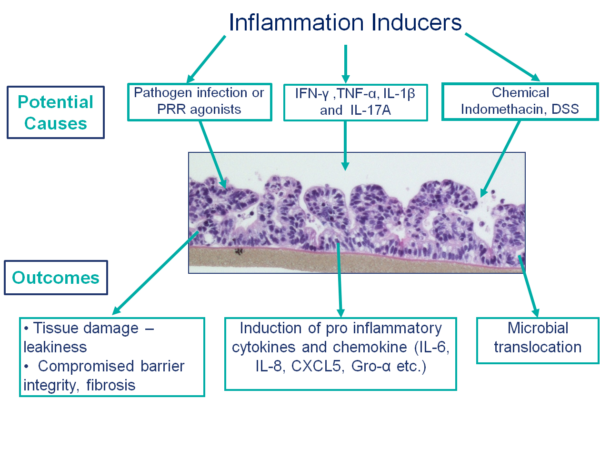
EpiIntestinal closely recapitulates the physiology, 3D tissue architecture, and function of the small intestine for use in key applications including inflammation and toxicity studies.
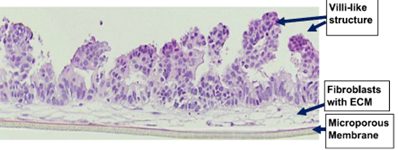
EpiIntestinal Full Thickness (SMI-FT) is a 3D reconstructed tissue model produced from normal, human cell-derived small intestine epithelial cells and fibroblasts. The highly differentiated tissue model is produced at the air-liquid-interface (ALI) in easy-to-handle tissue culture inserts. Structural analysis of the tissue model demonstrates columnar shaped basal cells and Kerckring folds. Ultrastructurally, EpiIntestinal exhibits brush borders, functional tight junctions and mucous secreting granules, similar to in vivo tissue.
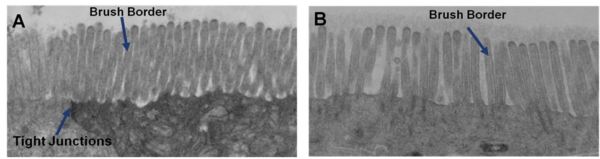
Transmission electron micrograph (TEM) of in vitro EpiIntestinal (A) and Explant tissues (B) showing Brush borders (situated at the luminal pole of the enterocyte) and tight junctions. Brush border – provides digestive and absorption surface; site for enzymes & transporters.
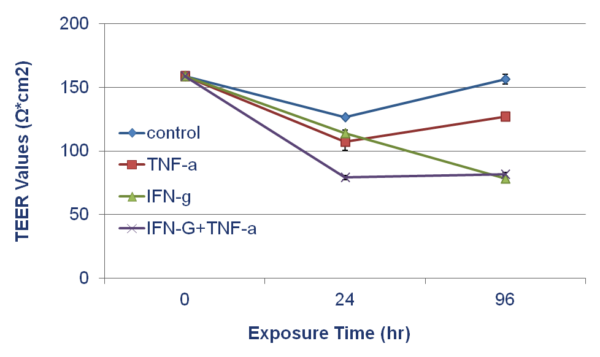
Effect of Inflammatory Signals on EpiIntestinal Barrier: TEER values of SMI-100-FT tissue following 96 hr. exposure to TNF-α (40 ng/ml), IFN-y (10 ng/ml), and TNF-α + IFN-y. Medium treated wells were used as untreated controls.
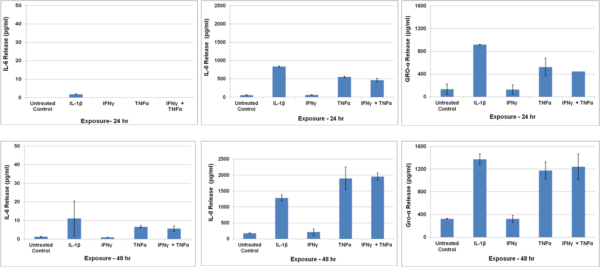
Cytokine release by SMI-100-FT tissues following exposure to inflammatory cytokines: Tissues were exposed for 24 or 48 hr to IL-1β (5 ng/ml) or TNF-α (40 ng/ml) + IFN-y (5 ng/ml) and culture supernatants were analyzed using Bio-Plex ELISA.
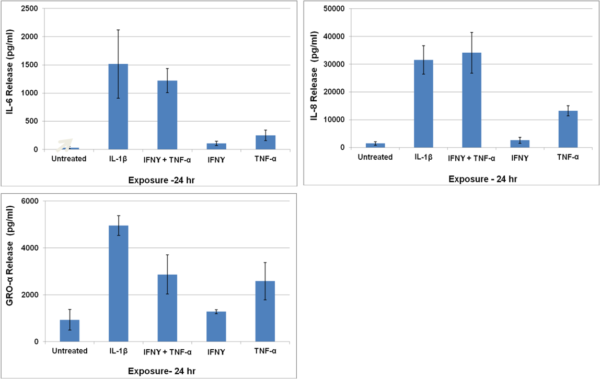
Cytokine release by EpiIntestinal following exposure to inflammatory stimuli: SMI-100-FT tissues were exposed for 24 hr to IL-1β (5 ng/ml) or TNF-α (40 ng/ml) + IFN-y (5 ng/ml). Culture supernatants were analyzed using Bio-Plex ELISA.
MatTek’s small intestine in vitro tissue model provides more human-relevant results in applications of drug safety and inflammation research. Availability of an easy-to-use, economical, and reproducible 3D reconstructed human SMI tissue will reduce animal use, minimize the number of test compounds dropped due to permeation problems in Caco-2, and significantly improve the prediction potential for drug absorption or inflammation in humans for candidate pharmaceutical compounds.
For more information, view the EpiIntestinal and References pages.
Thank you for requesting information about MatTek products! A representative will contact you shortly.
**If you would like to place an order for MatTek products, please contact Customer Service**
Get MatTek offers and updates delivered to your inbox.