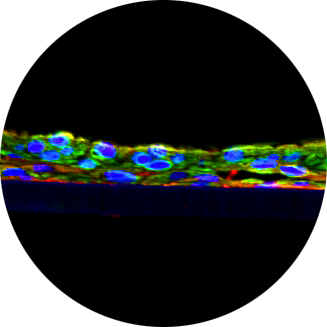
Micronucleus Induction by 5-Methoxypsoralen in the Photo Reconstructed Skin Micronucleus Assay: Development of a Human-Relevant NAM for Identifying Photo-genotoxic Substances
- TR Number: 1090
- Authors: Raabe, Hans, Creelman, Megan, Hewitt, Nicola, Irizar, Amaia, Lear, Emma, Nabua, Courtney, Wilt, Nathan, Pfuhler, Stefan
- Keywords: EpiDerm (EPI-200-MNA), hazard assessment, Micronucleus assay, Reconstructed Skin micronucleus test (RSMN), photo-activation, photo-genotoxicity, 8-methoxy psoralen. 8-MOP, 5-MOP, Sparfloxacin, mitomycin C, acetone, UVA/UVB, H1 filter
- Materials Tested: 8-methoxy psoralen. 8-MOP, 5-MOP, Sparfloxacin, mitomycin C, acetone, UVA/UVB
- Link to Article: https://iivs.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/Micronucleus.pdf
To address a lack of suitable non-animal tools to screen novel ingredients in personal care products for mutagenic/clastogenic activity after solar light exposure, we initiated a three-phase program to develop a new approach methodology (NAM) which integrates established UVA/UVB/visible light (UV/vis) photo-activation techniques to the reconstructed skin micronucleus (RSMN) assay. The first phase of the program established a repeat exposure photo irradiation schedule in reconstructed human epidermal (RhE) tissues, and the second phase was conducted to identify a photo-genotoxic substance for use as a positive control in subsequent third phase studies focused upon test method evaluations. An ideal positive control should be non-mutagenic in the absence of photo-activation, but is recognized to have human-relevant photo-induced mutagenic or carcinogenic etiology or, at minimum, is known to induce micronuclei in replicating mammalian cells after photo-irradiation