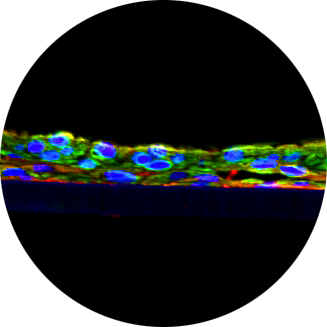
HUREL® Micro Livers
Self-assembling co-cultures (SACCs) of primary hepatocytes that are cryopreserved and combined with a non-parenchymal (stromal) cell line.
Our Product at a Glance
HUREL® micro livers are self-assembling co-cultures (SACCs) of primary hepatocytes that are cryopreserved and combined with a non-parenchymal (stromal) cell line. The hepatocytes spontaneously self-assemble into colonies. This patented form of liver cell culture has been demonstrated, in peer-reviewed studies, to produce the longest-enduring, most phenotypically stable and metabolically competent of any liver tissue construct developed in the world to date.
Metabolic Competency
The HUREL Micro Liver’s superior metabolic competency, derived in part from their multi-fold greater hepatocyte number and therefore greater cell density within the microtiter well, is the characteristic most centrally responsible for HUREL’s delivering data of superior translational predictivity for DMPK studies.
Phenotypically Stable
Rock-solid, long-enduring phenotypic stability creates the foundation for the superior metabolic competency that distinguishes data generated on the HUREL platform from that of primary hepatocytes cultured in suspension, in monoculture, in micropatterned arrays, and in 3D spheroids.
Peer Reviewed & Validated
The HUREL micro liver models have been used in dozens of publications to date by the world’s leading pharmaceutical companies and are integral to services at many contract research organizations.
Read publications by clicking here.
HUREL Liver Model Species
Each package will arrive with the following items inside: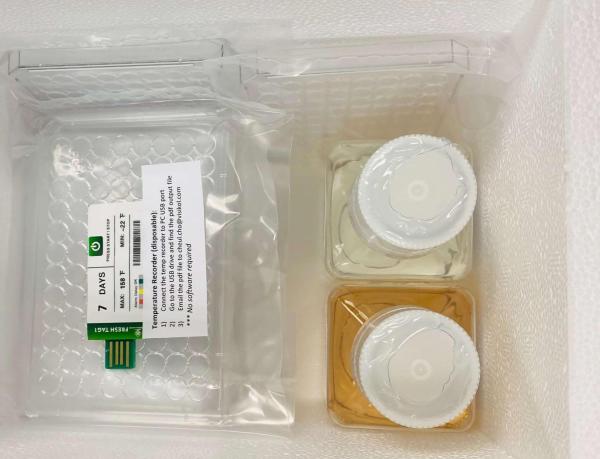
- Plated Cells
- Dosing & Maintenance Media
- Spare Lids
- Heat Packs
- Temperature Log
- Usage Instructions
Usage Protocols
HUREL® hepatic co-culture plates are shipped in a uniquely designed configuration to ensure temperature control and leakage prevention for the duration of shipment. Kindly follow our unpacking protocol for optimal use of our product.
Package Contents:
- HUREL maintenance media (serum-containing media): 65ml per plate
The serum-containing maintenance media is recommended to use for media change upon plate arrival and maintaining the culture plates (change media every 2 days) prior to assays. For long-term assays (> 7 day culture), the maintenance media is recommended to use for cell stability. - HUREL dosing media (serum-free media): 65ml per plate
The serum-free dosing media is recommended to use for assays that take up to 7 days. For drug clearance and metabolite generation assays, the media don’t need to be changed up to 7 days. - HUREL® co-culture plates, Replacement lids, Unpacking & Maintenance Protocol, COA lot information, Packing slip
- Temperature recorder* (disposable):
1) Connect the temp recorder to PC USB port, 2) Go to the USB drive and find the pdf output file, 3) Email the pdf output file to cheul.cho@visikol.com
*No software required. The temp. recorder will generate pdf output file automatically in the USB drive once connected
Recommended Aspiration Protocol
- Medium aspiration should be performed using a low vacuum pressure
- Aspirator tips should NEVER touch the bottom of the wells
- To ensure cells do not dry out and function and viability are sustained, it is recommended to aspirate and replace medium 3-6 columns at a time
Unpacking HUREL Plate:
- Open the cell culture plate from the sleeve and remove the rubber bands
- Remove the lid
- Peel off the sealing film
HUREL Human Pool™/ HUREL Human™/ HUREL Primate™/HUREL Rabbit™/ HUREL Cat™
|
Plate Format |
Hepatocyte Number/Well |
Recommended |
|---|---|---|
| 384-well | 11,000 | 30-50 μL |
| 96-well | 30,000 | 80-100 μL |
| 48-well | 70,000 | 180-200 μL |
| 24-well | 188,000 | 400-500 μL |
| 12-well | 375,500 | 800-1000 μL |
| 6-well | 940,000 | 2000-2400 μL |
HUREL Dog™
|
Plate Format |
Hepatocyte Number/Well |
Recommended |
|---|---|---|
| 384-well | 15,000 | 30-50 μL |
| 96-well | 40,000 | 80-100 μL |
| 48-well | 94,000 | 180-200 μL |
| 24-well | 250,000 | 400-500 μL |
| 12-well | 500,000 | 800-1000 μL |
| 6-well | 1,250,000 | 2000-2400 μL |
HUREL Rat SD™/ HUREL Rat WH™/ HUREL Minipig™
|
Plate Format |
Hepatocyte Number/Well |
Recommended |
|---|---|---|
| 384-well | 8,000 | 30-50 μL |
| 96-well | 25,000 | 80-100 μL |
| 48-well | 59,000 | 180-200 μL |
| 24-well | 156,000 | 400-500 μL |
| 12-well | 312,500 | 800-1000 μL |
| 6-well | 780,000 | 2000-2400 μL |
HUREL Mouse™
| Plate Format |
Hepatocyte Number/Well |
Recommended |
|---|---|---|
| 384-well | 7,000 | 30-50 μL |
| 96-well | 20,000 | 80-100 μL |
| 48-well | 47,000 | 180-200 μL |
| 24-well | 125,000 | 400-500 μL |
| 12-well | 250,000 | 800-1000 μL |
| 6-well | 625,000 | 2000-2400 μL |
HUREL Applications & Services
Cytotoxicity-Hepatotoxicity Screen DILItrain™
Our cytotoxicity and hepatotoxicity screening service makes early, high-acuity assessment of hepatotoxic risk cost-effective and thereby brings new illumination to the challenge of reducing late-stage candidate attrition.
HUREL® Flux™ Service
Hepatobiliary research services based on a new, patent-pending efflux transporter assay method. Transporters can play an important role in the clearance and excretion of the parent drug and/or its metabolite(s) into the bile canaliculus.
Metabolic Stability
The HUREL micro liver coculture system is a robust and reliable method for human in vivo clearance prediction and metabolite detection of slowly metabolized drugs.
Metabolite Identification (MetID) Services
HUREL micro livers produce robust metabolite yields that closely correlate to metabolites generated by parent compounds in vivo.
Multi-Parameter Toxicity-HUREL Tox™
Our Multi-Parameter Toxicity assay’s apply HUREL’s superior metabolic competency to a panel of complementary assays, creating a multi-parametric characterization of hepatotoxic risk.
Reaction Phenotyping Assay
Using HURELhumanPool™ primary hepatocyte micro liver model, intrinsic clearance rates for parent drug depletion in the absence and the presence of CYP inhibitors are measured to determine the contribution of CYP enzymes.
Viral Liver Disease Modeling-HUREL Viral™
The HUREL Viral™ platform aids the study of viral persistence and accelerates the development of antiviral drugs.