Get the latest
Get MatTek offers and updates delivered to your inbox.
The renal proximal tubular region is the most common site for a compound-specific kidney injury and is responsible for essential kidney functions, including reabsorption of low molecular weight proteins, solutes, and glucose, secretion of acids, and clearance of administered medications. The EpiKidney model is designed to replicate this region of the kidney.
In the advanced cell culture space, the kidney is one of the more underrepresented models due to its complexity from a function, physiology, and structure perspective. At MatTek, we are focused on building highly relevant in vitro organ systems and our EpiKidney model is a 3D lab-grown human tissue model designed to recapitulate the kidney within an easy-to-use in vitro system.
Real-time qPCR analysis confirms that the EpiKidney tissue expresses a panel of PTEC-specific markers that are necessary for renal clearance, secretion, and reabsorption: aminopeptidase CD13, multidrug resistance proteins MRP2/4, CYP450 enzymes, glucose transporters SGLT1/2, multidrug and toxin extrusion transporter MATE1, organic cation and anion transporters OCT1/2, OCTN1/2, and OATP4C1, urate transporter URAT1, and sodium phosphate co-transporter NP2. The model has demonstrated the tissue morphology, barrier properties, gene expression, and tissue performance seen within the in vivo proximal tubular region which enables it to be a highly useful model for kidney research.
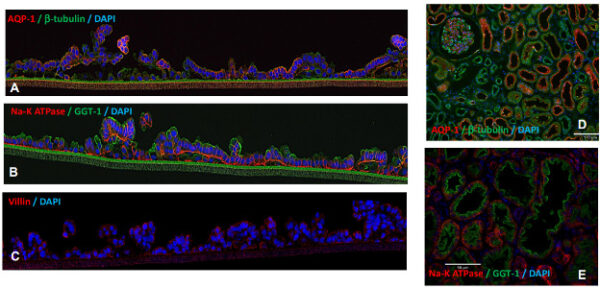
Evaluation of kidney-specific marker expression. Immunohistochemical staining of
EpiKidney tissue sections (day 16) (A-C) and kidney explant tissue (cortical region) (D-E); crosssections; imaged with ECHO microscope, 10X. Polarized PT epithelium expressing water channel
AQP-1, brush border Villin and GGT1 proteins on the apical side and sodium-potassium ATPase
pump on the basolateral side.
We have designed the model to be applicable for a broad range of applications from evaluating renal clearance of drugs (DMPK) to modeling chronic kidney disease (CKD) and evaluating kidney specific toxicity which accounts for 10% of preclinical and clinical stage failures.
Download the EpiKidney Protocol
Use EpiKidney to determine relative safety of drug formulations using the MTT and TEER assays and inflammatory responses.
Use EpiKidney to evaluate renal clearance of drugs, environmental compounds, and endogenous molecules.
EpiKidney mechanisms including tubular secretion and reabsorption allow researchers to study the effects of drug-drug interactions.
Kit: EpiKidney kits (Part Number: KID-100) consist of 24 individual tissues. Each kit contains tissues, culture medium (to support post-shipment equilibration of the tissues and experiments for 48 hours), and plasticware. Please contact MatTek Customer Service for specific kit contents.
Formats:
Culture: Air-liquid interface/ wet film
Lot numbers: Tissue lots produced each week are assigned a specific lot number. A letter of the alphabet is appended to the end of the lot number to differentiate between individual sets of 24 tissues within a given production lot of tissues. All tissue kits within a production lot are identical in regard to cells, medium, handling, culture conditions, etc.
Shipment: At room temperature on medium-supplemented, agarose gels
Shipment day: Every Monday
Delivery: Tuesday morning via FedEx priority service (US). Outside US: Tuesday-Wednesday depending on location.
Shelf life: Including time in transit, tissues may be stored at room temperature (RT) for up to 3 days. However, the best reproducibility will be obtained if tissues are used consistently on the same day, e.g. Tuesday afternoon or following overnight storage at RT (Wednesday morning).
Length of experiments: Tissue cultures can be continued for ONE (1) MONTH or more with good retention of normal tissue morphology. Tissues must be fed every other day with 5.0 mL of maintenance medium (KID-100-MM) in the basal compartment and with 100 μL of KID-100-MM applied topically. Cell culture inserts with Hanging top 12-well plates (HNG-TOP-12) allow use of 5.0 mL of KID-100-MM per feeding.
Type: Human proximal tubule epithelial cells (hPTEC)
Genetic make-up: Single donor
Derived from: Healthy adult donor
Alternatives: Alternate donors available upon request
Screened for: HIV, Hepatitis-B, Hepatitis-C, mycoplasma
Base medium: DMEM/F12
Growth factors/hormones: Epidermal growth factor and other proprietary factors
Antibiotics: Penicillin/streptomycin (100 U/mL / 100 µg/mL)
Anti-fungal agent: None
pH Indicator: Phenol red
Other additives: Proprietary
Alternatives: Phenol red-free and antibiotic-free tissues are available. Agents are removed at least 3 days prior to shipment.
Visual inspection: All tissues are visually inspected and if physical imperfections are noted, tissues are rejected for shipment.
Sterility: All media used throughout the production process is checked for sterility. Maintenance medium is incubated with and without antibiotics for 1 week and checked for sterility. The agarose gel from the 24-well plate used for shipping is also incubated for 1 week and checked for any sign of contamination.
Screening for pathogens: All cells are screened and are negative for HIV, hepatitis B and hepatitis C using PCR. However, no known test method can offer complete assurance that the cells are pathogen free. Thus, these products and all human derived products should be handled at BSL-2 levels (biosafety level 2) or higher as recommended in the CDC-NIH manual, “Biosafety in microbiological and biomedical laboratories,” 1998. For further assistance, please contact your site Safety Officer or MatTek technical service.
Notification of lot failure: If a tissue lot fails QC or sterility testing, the customer will be notified and the tissues will be replaced without charge. Because our QC and sterility testing is done post-shipment, notification will be made as soon as possible (Under normal circumstances, TEER failures will be notified by Thursday 5 p.m.; sterility failures will be notified within 8 days of shipment)
Thank you for requesting information about MatTek products! A representative will contact you shortly.
**If you would like to place an order for MatTek products, please contact Customer Service**
Get MatTek offers and updates delivered to your inbox.